top of page
Extensor Mechanism of the Knee: Structure, Trauma, and Treatment
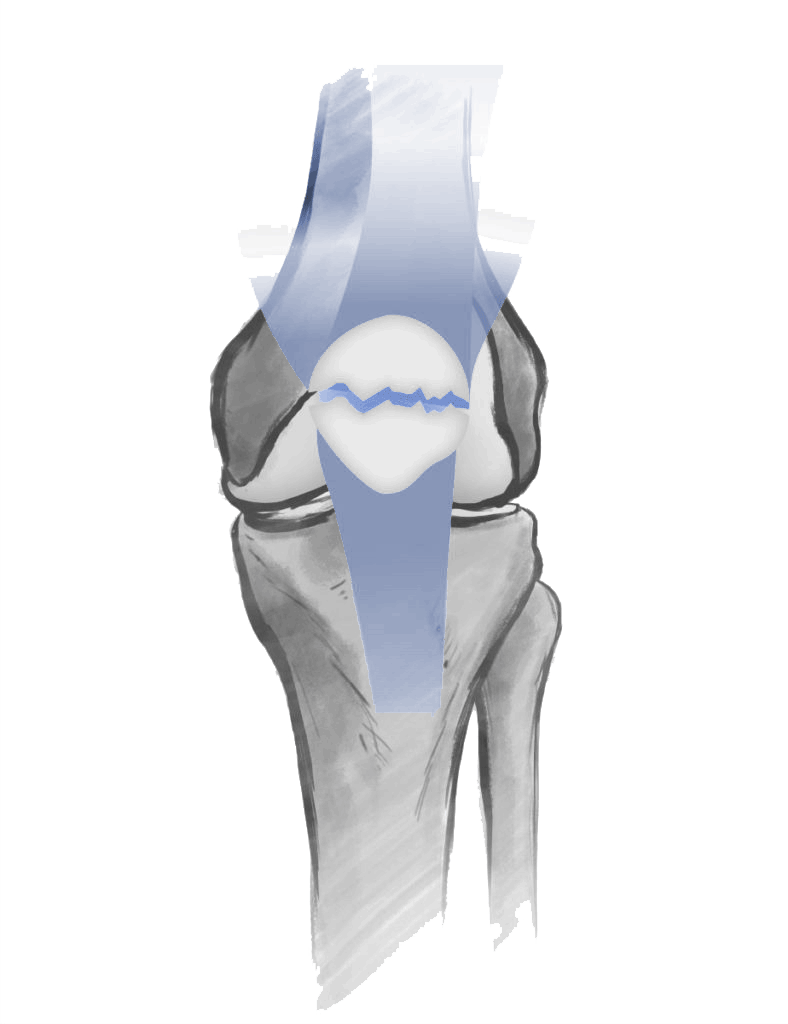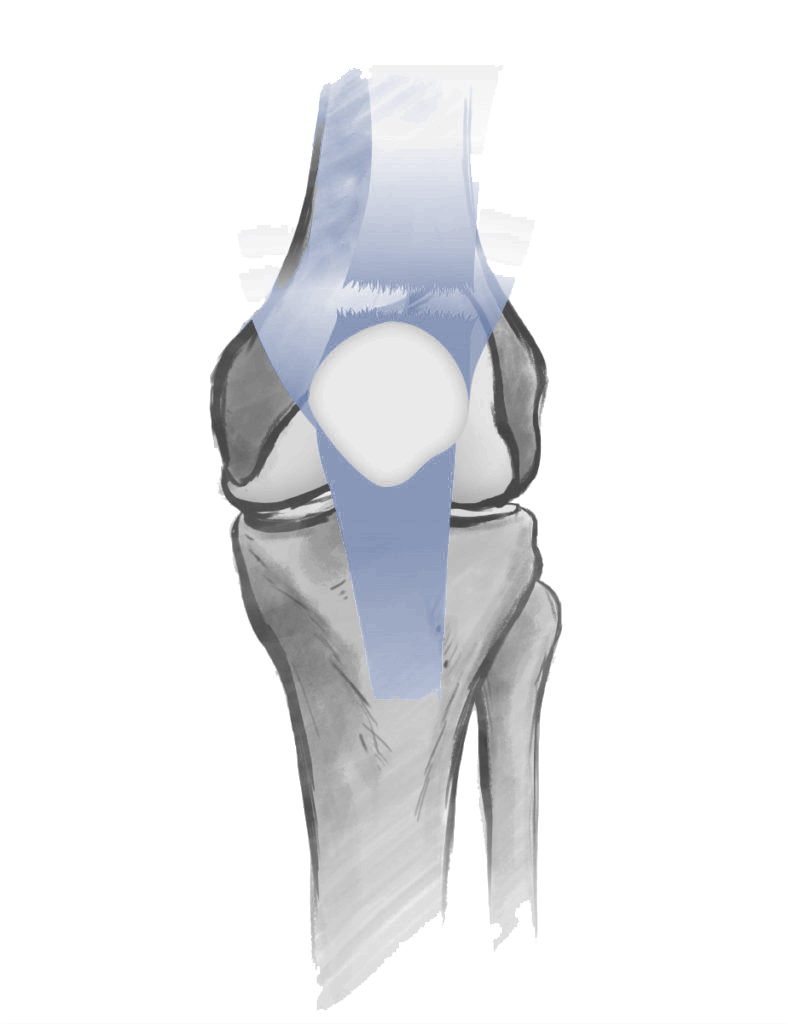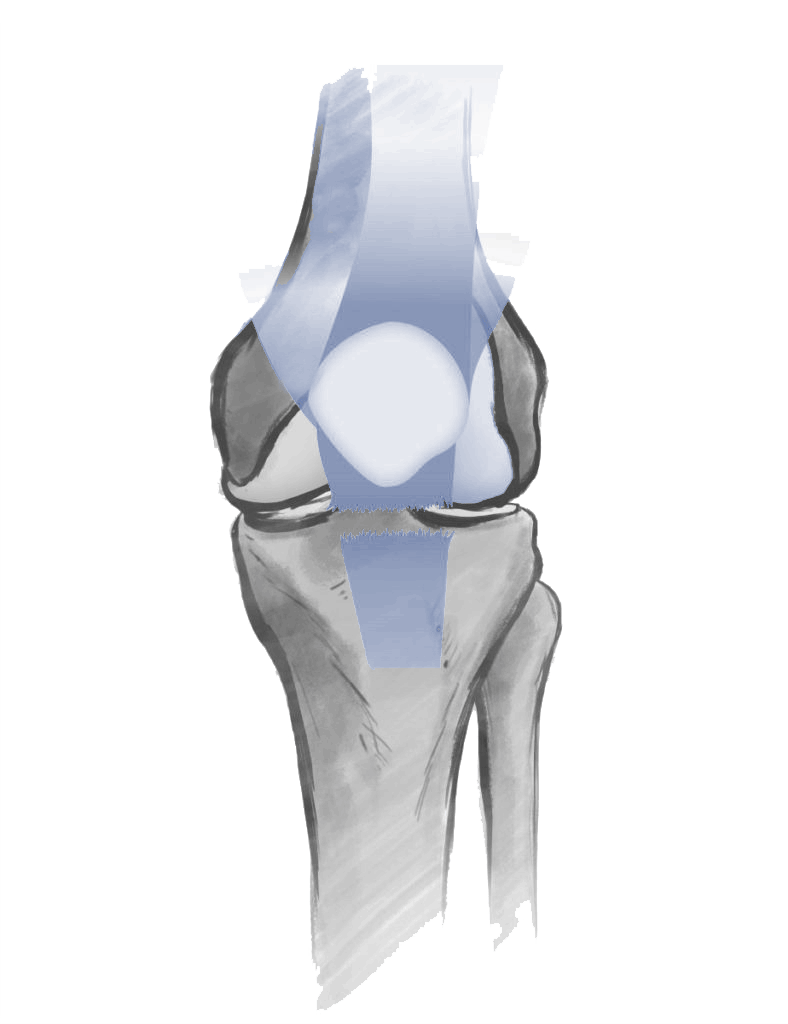
The extensor mechanism of the knee is essential for knee mobility and is made up of three main components that work together to enable active knee extension: the patella (kneecap), the quadriceps tendon, and the patellar tendon.
Structure and Function
-
Patella (Kneecap): A small bone that acts as a pulley between the quadriceps tendon and patellar tendon, increasing the efficiency of the knee’s extensor mechanism.
-
Quadriceps Tendon: Connects the quadriceps muscle to the patella and helps transmit force during knee extension.
-
Patellar Tendon: Links the patella to the tibia and is crucial for transferring the force generated by the quadriceps to extend the knee.
TREATMENT
01. NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
-
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding weight-bearing activities that strain the knee.
-
Bracing or Immobilization: To provide support and limit movement, allowing healing of minor injuries.
-
Physical Therapy: To maintain muscle strength and knee function while preventing stiffness.
-
Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation control.
02. SURGICAL TREATMENT
-
Repair or Reconstruction: Surgical intervention is often required for significant tears or ruptures of the patellar tendon, quadriceps tendon, or other components of the extensor mechanism.
-
Patellar Tendon Repair: In cases of complete tears or avulsion fractures.
-
Quadriceps Tendon Repair: In cases of ruptures or tears of the quadriceps tendon, often in older patients.
-
-
Tendon Grafting: In severe cases, tendon grafts may be used to reconstruct the damaged extensor mechanism.
03. POST-SURGICAL REHABILITATION
-
Focus on restoring knee strength, mobility, and function through a gradual rehabilitation program.
-
Full recovery can take 3-6 months, depending on the severity of the injury and the type of surgery performed.
04. KEY POINT
-
Early intervention is critical, with non-surgical treatment suitable for minor injuries and surgery necessary for more severe or complete ruptures. Rehabilitation is crucial for restoring function and strength to the knee.
bottom of page
